5 Warehouse RL Week 2: IPPO Comparison
5.1 Overview
Trained and compared two IPPO implementations on rware-tiny-2ag-v2 (2 robots, 8x8 grid, 4 packages):
- Vanilla IPPO: EPyMARL baseline with exploration tuning
- Advanced IPPO: Custom implementation with macro-actions and behavioral cloning
5.2 Methods
5.2.1 Vanilla IPPO (EPyMARL)
Standard Independent PPO with increased entropy for exploration.
Key Hyperparameters:
entropy_coef: 0.1 (3x higher than default)lr: 0.0001buffer_size: 1024batch_size: 256hidden_dim: 96epochs: 4gae_lambda: 0.95- Training steps: 20M
5.2.2 Advanced IPPO (Custom)
Enhanced IPPO with macro-actions and warm-start.
Key Features:
- Macro-actions: Agent commits to each action for 4 steps, making it easier to learn which actions led to success
- Behavioral cloning: Pre-train agents by copying simple rule-based strategies to give them a head start
- EMA actors: Use smoothed version of learned policy for more stable testing performance
- Entropy floor: Keep agents exploring new behaviors throughout training to avoid getting stuck
- Dynamic clip decay: Gradually reduce how much the policy can change per update as learning progresses
Key Hyperparameters:
lr: 0.0003batch_size: 256hidden_dim: 128epochs: 10entropy_coef: 0.01- Training steps: 5M
5.3 Results
5.3.1 Return Mean Comparison
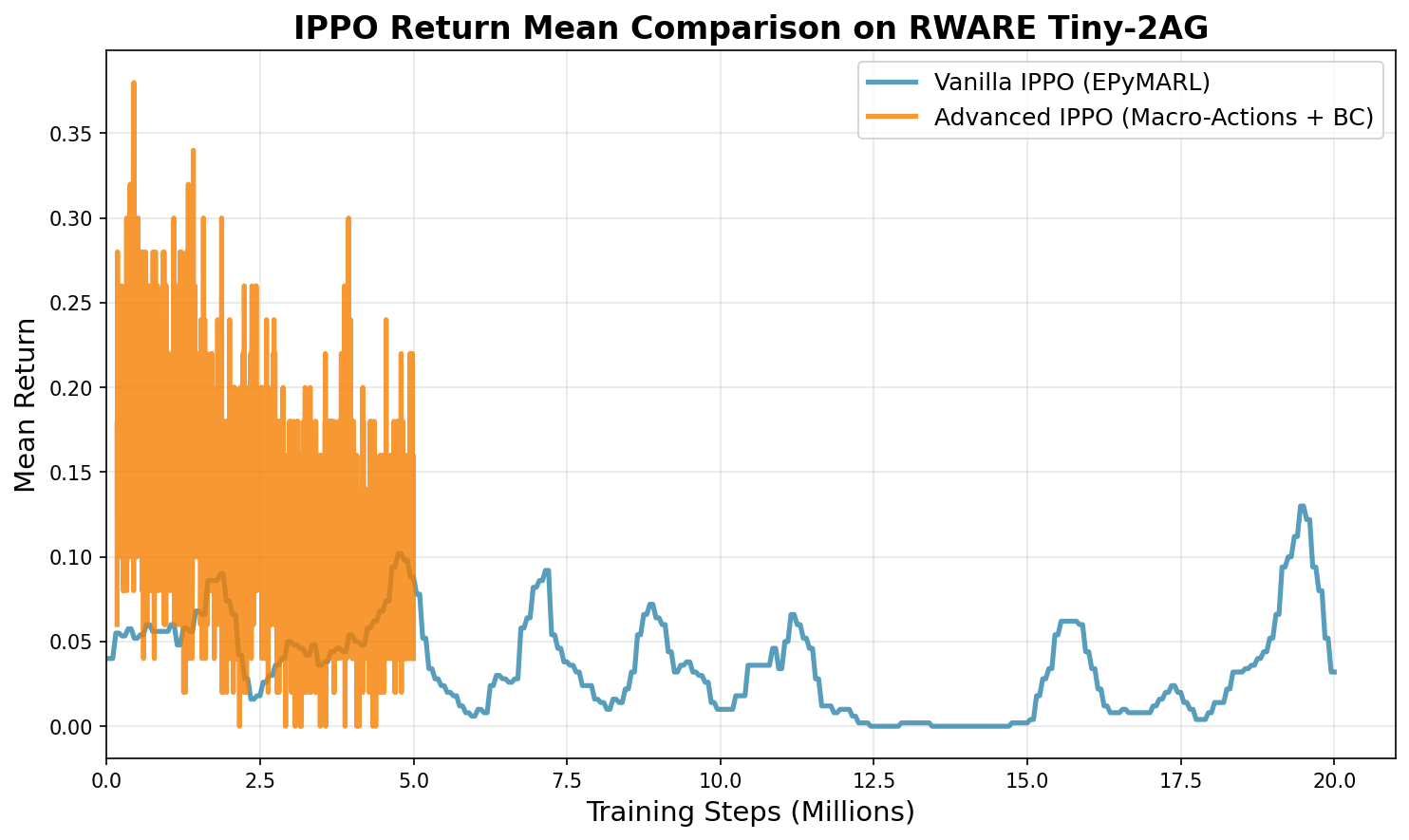
Vanilla IPPO (20M steps):
- Final: 0.032
- Peak: 0.130
Advanced IPPO (5M steps):
- Final: 0.040
- Peak: 0.380
5.4 Key Findings
- Exploration matters: Vanilla IPPO required 3x higher entropy (0.1 vs 0.03) to prevent premature convergence
- Advanced features help: Macro-actions and BC warm-start achieved 3x better peak return (0.38 vs 0.13)
- Sample efficiency: Advanced IPPO reached peak performance in 4x fewer steps (5M vs 20M)
- Stability issues: Both approaches showed performance degradation over extended training
5.5 Conclusion
Advanced IPPO with macro-actions and BC warm-start significantly outperformed vanilla IPPO in both sample efficiency and peak performance. The advanced implementation achieved:
- 3x better peak return (0.38 vs 0.13)
- 4x better sample efficiency (peak at 5M vs 20M steps)
However, both implementations face stability challenges requiring further investigation into:
- Reward shaping
- Curriculum learning
- Value function clipping
- Exploration scheduling